The ROI of CRM: How to Measure the Impact on Your Bottom Line – sounds kinda boring, right? Wrong! Unlocking the true potential of your CRM isn’t about endless spreadsheets; it’s about smarter strategies and tangible results. This isn’t just about tracking numbers; it’s about understanding how your customer relationships directly translate to profit. We’re diving deep into the nitty-gritty of measuring CRM effectiveness, showing you how to pinpoint exactly where your CRM shines (and where it needs a serious upgrade).
From defining core CRM functionalities and identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) to analyzing the impact on sales and customer service, we’ll equip you with the tools and insights to calculate your CRM’s ROI and maximize its potential. We’ll even explore future trends in CRM technology and how they’ll shape your bottom line. Get ready to transform your CRM from a data dumping ground into a profit-generating machine.
Defining CRM and its Core Functions
Source: surferseo.art
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are the backbone of modern business, enabling companies to effectively manage interactions with current and potential customers. They’re more than just contact lists; they’re powerful tools that streamline processes, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately, boost the bottom line. Understanding the core functions and various types of CRM systems is crucial for harnessing their full potential.
CRM systems centralize customer data, automating tasks and providing valuable insights. This allows businesses to personalize interactions, improve customer service, and identify valuable sales opportunities. At its core, a CRM system aims to improve customer relationships, leading to increased loyalty, repeat business, and ultimately, higher profits.
Core Functionalities of CRM Systems
The core functionalities of a CRM system revolve around managing and analyzing customer interactions throughout the entire customer lifecycle. This encompasses various aspects, from initial contact to post-sale support. Key functionalities include contact management, sales force automation, marketing automation, customer service management, and reporting and analytics. Contact management provides a centralized database of customer information, while sales force automation streamlines the sales process. Marketing automation facilitates targeted campaigns and personalized communications, and customer service management helps resolve customer issues efficiently. Finally, reporting and analytics provide insights into customer behavior and campaign performance. These functionalities work in concert to provide a holistic view of the customer journey.
Types of CRM Systems
CRM systems are broadly categorized into three types: operational, analytical, and collaborative. Operational CRMs focus on automating and improving day-to-day business processes related to customer interactions. Analytical CRMs concentrate on gathering and analyzing customer data to gain insights into customer behavior and preferences. Collaborative CRMs focus on improving communication and collaboration among different departments within a company to provide a unified customer experience. Many modern CRM systems integrate all three types, offering a comprehensive solution.
Examples of CRM System Utilization
A retail business might use a CRM system to track customer purchases, preferences, and interactions across various channels (online, in-store, phone). This data allows them to personalize marketing campaigns, offer targeted promotions, and improve customer service by proactively addressing potential issues. A SaaS company could use a CRM to manage leads, track sales opportunities, and automate follow-up emails. This ensures that sales teams stay organized and efficient, ultimately leading to faster sales cycles and higher conversion rates. A financial institution might use a CRM to manage customer accounts, track transactions, and provide personalized financial advice. This helps build strong customer relationships and fosters loyalty. The applications are virtually limitless, tailored to the specific needs of each industry and business.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for CRM Success
Measuring the return on investment (ROI) of your CRM system isn’t just about crunching numbers; it’s about understanding how well your CRM aligns with your business goals and contributes to your bottom line. Choosing the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is crucial for this. By tracking the right metrics, you gain valuable insights into your CRM’s effectiveness and can make data-driven decisions to optimize its performance.
Knowing which KPIs to focus on can feel overwhelming, but focusing on a few key areas provides a clear picture of your CRM’s impact. This section Artikels five crucial KPIs and demonstrates how to track them, setting realistic targets and identifying data sources.
Five Crucial KPIs for CRM Effectiveness
Selecting the right KPIs is vital for assessing your CRM’s success. Focusing on a few key metrics provides a clearer, more actionable understanding of your CRM’s contribution to overall business objectives than trying to track everything at once. These five KPIs offer a comprehensive view of your CRM’s performance.
| KPI | Measurement Method | Target Value (Example) | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Total marketing and sales costs / Number of new customers acquired | $500 per customer (This will vary greatly depending on your industry and business model) | Marketing automation platform, sales CRM, accounting software |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | Average purchase value x Average purchase frequency x Average customer lifespan | $5000 per customer (This is an example and should be adjusted based on your business) | Sales CRM, accounting software, customer behavior analysis |
| Customer Churn Rate | (Number of churned customers / Total number of customers at the beginning of the period) x 100 | <10% (This is a desirable target, but the acceptable rate depends on the industry) | Sales CRM, customer support ticketing system |
| Sales Conversion Rate | Number of closed-won deals / Number of qualified leads | 25% (This is an example and varies significantly by industry and sales process) | Sales CRM, marketing automation platform |
| Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score | Average score from customer satisfaction surveys | 4.5 out of 5 stars (This is a target; the ideal score will depend on your industry and survey design) | Customer feedback surveys, CRM-integrated feedback tools |
Aligning KPIs with Overall Business Objectives
The importance of aligning your CRM KPIs with your broader business objectives cannot be overstated. KPIs should directly reflect the key goals you’re trying to achieve. For example, if your primary objective is to increase market share, your KPIs might focus on lead generation and conversion rates. If your goal is to improve customer retention, you’ll prioritize metrics like customer churn rate and CLTV.
Without this alignment, you risk tracking metrics that don’t actually contribute to your business success. By carefully selecting KPIs that directly support your strategic goals, you can ensure your CRM efforts are truly driving value. A company aiming for rapid growth might focus on CAC and sales conversion rate, while a company focused on long-term customer relationships will emphasize CLTV and CSAT. This strategic alignment ensures that the data you collect is relevant and actionable, guiding your CRM strategy and resource allocation effectively.
Quantifying the Impact of CRM on Sales

Source: crmguides.com
Measuring the return on investment (ROI) of your CRM system isn’t just about guessing; it’s about digging into the data and uncovering the tangible benefits. By meticulously tracking key sales metrics, you can demonstrably prove the value your CRM brings to the bottom line. This involves a strategic approach to data collection and analysis, allowing you to confidently showcase the positive impact of your CRM implementation.
Tracking sales improvements linked to CRM usage requires a multi-faceted approach. It’s not simply about comparing overall sales figures before and after implementation. Instead, you need to pinpoint specific actions within the CRM system that directly contribute to increased sales. This granular level of analysis allows for a more precise understanding of the ROI and highlights areas where the CRM excels and areas that might need further optimization.
Methods for Tracking Sales Improvements Attributed to CRM Usage
Effective CRM tracking involves focusing on several key areas. First, monitor lead conversion rates. How many leads generated through your CRM actually convert into paying customers? This metric directly reflects the effectiveness of your sales process as facilitated by the CRM. Second, analyze sales cycle length. Does the CRM help shorten the time it takes to close a deal? A reduction in sales cycle length translates directly into faster revenue generation. Finally, track average deal size. Does the CRM help your sales team close larger deals? This could be due to better lead qualification or more effective upselling/cross-selling opportunities identified within the CRM. By tracking these three key metrics, you can build a compelling case for the CRM’s positive impact.
Sales Performance Comparison: Before and After CRM Implementation
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario. “Acme Corp” experienced an average of 50 sales per month with an average deal size of $1,000 before implementing their CRM. Their total monthly revenue was $50,000. After implementing a CRM and optimizing their sales process, Acme Corp saw a significant increase. Their monthly sales jumped to 75, with an average deal size increasing to $1,200. This resulted in a monthly revenue of $90,000. This represents a significant 80% increase in monthly revenue directly attributable to improved sales efficiency facilitated by the CRM. While this is hypothetical, it demonstrates the potential for substantial ROI. Real-world results will vary depending on the specific CRM system, the industry, and the effectiveness of its implementation.
Illustrative Graph: CRM Adoption and Sales Growth
Imagine a line graph. The X-axis represents time, marked in months, starting from the month before CRM implementation (Month 0) and extending to several months afterward. The Y-axis represents monthly revenue in dollars. A dashed line represents monthly revenue *before* CRM implementation, showing a relatively flat or slightly increasing trend. A solid line represents monthly revenue *after* CRM implementation. This line would show a noticeably steeper upward trend, clearly demonstrating the positive correlation between CRM adoption and increased sales. The point where the solid line diverges significantly from the dashed line visually represents the point where the CRM’s impact becomes clearly measurable. The steeper the incline of the solid line, the more significant the impact of the CRM on sales growth. The graph clearly visualizes the positive correlation and quantifies the improvement in sales revenue directly linked to CRM usage.
Analyzing the Influence of CRM on Customer Service
Let’s face it, happy customers are loyal customers, and loyal customers fuel your bottom line. A well-implemented CRM system isn’t just about managing contacts; it’s the secret weapon to transforming your customer service game. By centralizing customer information and streamlining processes, CRM significantly boosts efficiency and satisfaction, leading to measurable improvements in your business.
CRM systems enhance customer service efficiency and satisfaction by providing a 360-degree view of each customer. This means support agents have immediate access to past interactions, purchase history, and even notes from previous conversations. This holistic view empowers agents to provide faster, more personalized, and ultimately more effective support. Imagine a customer calling about a faulty product; with CRM, the agent can instantly see the purchase date, warranty information, and even previous attempts at troubleshooting – resolving the issue swiftly and efficiently. This personalized touch fosters customer loyalty and minimizes frustration.
Metrics Reflecting Improved Customer Service
The impact of CRM on customer service isn’t just anecdotal; it’s measurable. Tracking specific metrics provides concrete evidence of the positive influence of your CRM investment. These metrics allow you to identify areas for improvement and demonstrate the return on investment.
- Reduced Resolution Time: CRM streamlines workflows, allowing agents to access information quickly and resolve issues faster. For example, a company might see a 20% reduction in average resolution time after implementing a CRM system, translating to significant cost savings and improved customer satisfaction. This reduction can be calculated by comparing average resolution times before and after CRM implementation.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction Scores (CSAT): Happier customers translate to better reviews, increased loyalty, and ultimately, more revenue. Tracking CSAT scores through surveys or feedback forms reveals the direct impact of improved service. A company implementing a new CRM system might see a 15% increase in CSAT scores within six months, showcasing the positive impact on customer perception.
- Reduced Customer Churn: By proactively addressing customer issues and providing personalized support, CRM helps reduce customer churn. Analyzing churn rates before and after CRM implementation can reveal the financial benefits of improved customer retention. For instance, a company may see a 10% decrease in churn rate after implementing CRM, leading to significant cost savings from retaining existing customers.
- Improved First Contact Resolution (FCR): CRM allows agents to access a complete history of customer interactions, leading to a higher rate of resolving issues on the first contact. This metric directly reflects efficiency gains and improved customer experience. An improvement in FCR from 60% to 75% indicates a significant increase in efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Measuring the Return on Investment (ROI) of CRM: The ROI Of CRM: How To Measure The Impact On Your Bottom Line
Source: semrush.com
Calculating the return on investment for a CRM system isn’t just about crunching numbers; it’s about understanding how your CRM contributes to your business’s overall health. A well-implemented CRM system can significantly boost efficiency and profitability, but you need a clear method to demonstrate this value to stakeholders. This section explores various methods to accurately assess your CRM’s ROI and highlight both the readily apparent and less obvious benefits.
Methods for Calculating CRM ROI
Several approaches exist for calculating the ROI of a CRM system. The best method depends on your specific business goals and the data you have available. A simplistic approach might focus solely on the direct cost savings, while a more comprehensive analysis would incorporate intangible benefits.
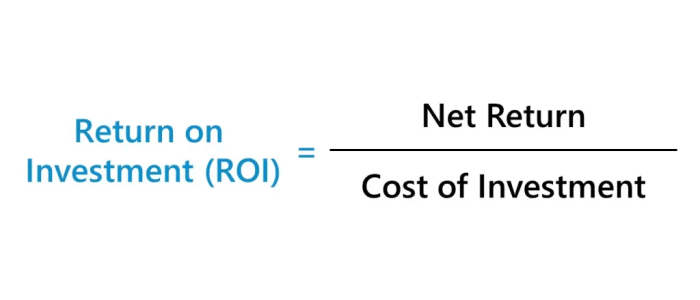
One common method involves comparing the total cost of the CRM implementation (software licenses, implementation fees, training, etc.) against the increased revenue or cost savings generated. This can be expressed as a percentage using the following formula:
ROI = [(Gain from Investment – Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment] x 100%
Another approach focuses on key performance indicators (KPIs) directly influenced by the CRM. For example, improved sales conversion rates, reduced customer churn, or faster resolution times for customer service issues can all be quantified and linked to the CRM’s impact.
Tangible and Intangible Benefits Contributing to CRM ROI
The value of a CRM system extends beyond easily quantifiable metrics. While tangible benefits like increased sales and reduced operational costs are readily apparent, intangible benefits like improved customer satisfaction and enhanced employee morale also contribute significantly to the overall ROI.
Tangible Benefits: These are easily measured and directly linked to financial outcomes. Examples include increased sales revenue due to improved lead management, reduced marketing costs through targeted campaigns, decreased customer service costs due to faster resolution times, and minimized operational expenses from streamlined processes.
Intangible Benefits: These are harder to quantify directly but significantly impact the business’s long-term success. Examples include improved customer satisfaction leading to increased customer loyalty and advocacy, better employee productivity and engagement due to improved tools and processes, enhanced brand reputation through consistent customer interactions, and improved decision-making based on data-driven insights provided by the CRM.
Hypothetical Case Study: Small Business CRM ROI
Let’s consider a small bakery, “Sweet Success,” that implements a CRM system for $5,000. Before the CRM, their average order value was $20, and they had a 10% conversion rate from leads to sales. After implementing the CRM, they improved their conversion rate to 20% and increased their average order value to $25 due to targeted promotions and better customer relationship management.
Assuming they generated 1000 leads in a year both before and after CRM implementation:
Before CRM: 1000 leads * 10% conversion rate * $20 average order value = $2000 revenue from leads
After CRM: 1000 leads * 20% conversion rate * $25 average order value = $5000 revenue from leads
Increased Revenue: $5000 – $2000 = $3000
Using the ROI formula:
ROI = [($3000 – $5000) / $5000] x 100% = -40%
In this scenario, the ROI appears negative. However, this calculation only considers the increased revenue from leads. It doesn’t factor in potential cost savings from improved efficiency in customer service, marketing automation, or reduced administrative overhead. A more comprehensive analysis incorporating these factors would likely reveal a positive ROI.
Improving CRM Effectiveness and Maximizing ROI
So, you’ve implemented a CRM. Fantastic! But the real work begins now. Getting a strong ROI from your CRM isn’t just about setting it up; it’s about consistently optimizing its performance and ensuring it aligns perfectly with your business goals. This section dives into the strategies you need to maximize your investment and truly reap the rewards.
Successfully leveraging a CRM requires proactive management and continuous improvement. Ignoring potential pitfalls can lead to underutilization and a disappointing return on investment. By addressing challenges head-on and implementing data-driven optimization strategies, you can transform your CRM from a costly software into a powerful engine for growth.
Addressing CRM Implementation Challenges, The ROI of CRM: How to Measure the Impact on Your Bottom Line
Implementing a CRM system often presents hurdles that can significantly impact its effectiveness. These challenges can range from user adoption issues to integration problems and data quality concerns. Addressing these proactively is crucial for maximizing ROI.
- Challenge: Poor user adoption. Employees might resist using the new system due to a lack of training, an unintuitive interface, or perceived added workload.
- Solution: Comprehensive training programs, ongoing support, and a user-friendly interface are essential. Highlight the benefits of using the CRM, focusing on how it simplifies their tasks and increases efficiency. Gather feedback regularly and adapt the system accordingly.
- Challenge: Integration difficulties. Connecting the CRM with other business systems (e.g., marketing automation, accounting software) can be complex and time-consuming.
- Solution: Invest in robust integration capabilities or seek expert assistance to ensure seamless data flow between systems. Prioritize integrations that deliver the most significant impact on your business processes.
- Challenge: Data quality issues. Inconsistent or inaccurate data renders the CRM useless for insightful analysis and decision-making.
- Solution: Establish clear data entry standards, implement data validation rules, and regularly clean and update your CRM data. Consider employing data cleansing tools to automate this process.
Optimizing CRM Data Quality and Utilization
High-quality data is the lifeblood of a successful CRM. Without accurate, complete, and consistently updated information, your CRM’s analytical capabilities are severely limited, hindering your ability to make informed decisions and track progress toward your goals.
Effective data management involves more than just inputting information. It requires a proactive approach that prioritizes data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility. This translates to better insights, more effective targeting, and ultimately, a higher ROI. For example, a company selling high-end audio equipment might use CRM data to identify customers who have previously purchased specific amplifier models and target them with promotions for compatible speakers. This targeted approach increases the likelihood of a sale compared to a generic marketing campaign.
Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting CRM Strategies
A “set it and forget it” approach to CRM management is a recipe for disaster. Regular review and adjustment are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and maximizing ROI. This requires a structured process that allows for continuous improvement and adaptation to changing business needs.
A quarterly review process, for example, could involve analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs), identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes to optimize the CRM’s effectiveness. This iterative approach ensures that your CRM remains a valuable asset, constantly evolving to meet the demands of your business. For instance, if sales conversion rates from a particular marketing campaign tracked within the CRM are low, the review process might identify the need to adjust the campaign’s targeting or messaging. This adaptive approach ensures that resources are not wasted on ineffective strategies.
Future Trends in CRM and their Impact on ROI
The CRM landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing customer expectations. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for businesses aiming to maximize their CRM ROI. Failing to adapt could mean falling behind competitors and missing out on significant opportunities for growth and efficiency. The following sections explore key trends and their impact on the bottom line.
Artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and the increasing focus on data-driven decision-making are reshaping how businesses interact with their customers. These advancements offer the potential to significantly improve efficiency, personalize customer experiences, and ultimately boost the return on investment from CRM systems.
AI-Powered CRM Enhancements
AI is rapidly transforming CRM, moving beyond simple automation to offer predictive capabilities and personalized interactions. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and predict customer behavior, enabling proactive engagement and improved sales forecasting. For example, AI can predict which leads are most likely to convert, allowing sales teams to prioritize their efforts and improve conversion rates. This leads to a direct increase in revenue and a stronger ROI. Furthermore, AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues, thus reducing customer service costs and improving satisfaction.
Automation Streamlining Processes
Automation is another key trend boosting CRM ROI. Automating repetitive tasks like data entry, lead qualification, and follow-up emails frees up valuable employee time, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities such as building relationships with customers and closing deals. Consider a company that automates its lead nurturing process. By using automated email sequences triggered by specific customer actions, they can nurture leads more efficiently, leading to a higher conversion rate and a better ROI on their CRM investment. This reduces operational costs and improves sales efficiency.
Data Analytics for Actionable Insights
Modern CRM systems are powerful data repositories. The ability to effectively analyze this data to gain actionable insights is critical for maximizing ROI. By tracking key metrics such as customer lifetime value (CLTV), customer churn rate, and marketing campaign effectiveness, businesses can identify areas for improvement and optimize their strategies. For example, a retail company analyzing CRM data might discover that customers who engage with their social media campaigns have a higher CLTV. This insight allows them to allocate more resources to social media marketing, leading to a better return on investment. This data-driven approach allows for continuous improvement and optimization.
Closure
Mastering the art of measuring your CRM’s ROI isn’t just about crunching numbers; it’s about building a data-driven strategy that fuels growth. By aligning your KPIs with business objectives, tracking key metrics, and adapting to emerging trends, you can unlock the true potential of your CRM and watch your bottom line soar. Don’t just manage your customers – strategically leverage them for sustainable success. The data’s there, waiting to be discovered; the profit’s waiting to be made.
